Hcooch ch2 h2o Everything You Need to Know About
hcooch ch2 h2o commonly known as methyl formate, is an organic compound widely used in chemical industries. This ester has a pleasant odor and plays a crucial role in various applications, including the manufacturing of perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and as an industrial solvent.
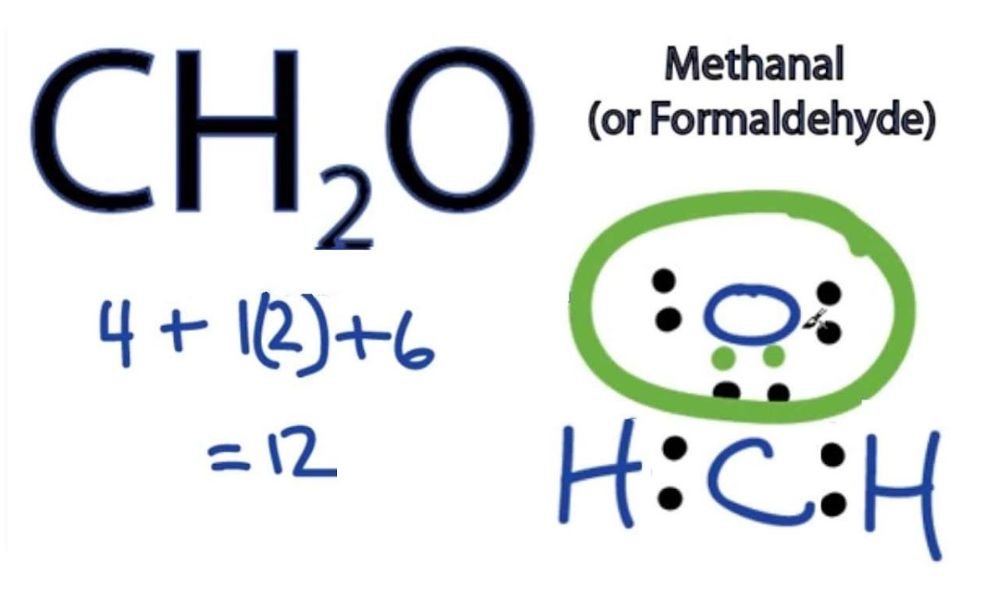
Chemical Composition and Structure
hcooch ch2 h2o consists of three main elements: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). It is classified as an ester because it forms from the reaction of an acid (formic acid) and an alcohol (methanol).
Molecular Formula and IUPAC Name
- Molecular Formula: hcooch ch2 h2o
- IUPAC Name: Methyl methanoate
Structural Breakdown
The molecular structure includes:
- A formate group (HCOO-), derived from formic acid
- A methyl (-CH₃) group, derived from methanol
Physical Properties
Understanding the physical properties of hcooch ch2 h2o is essential for handling and application.
- Appearance: A colorless liquid with a fruity odor
- Boiling Point: Around 31.5°C (88.7°F)
- Melting Point: -100°C (-148°F)
- Density: 0.97 g/cm³
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water but mixes well with organic solvents like alcohol and ether
Chemical Properties
Methyl formate exhibits various chemical behaviors depending on the environment.
Reactivity with Water
Methyl formate slowly hydrolyzes in water, forming methanol (CH₃OH) and formic acid (HCOOH). This reaction speeds up in the presence of acids or bases.
Combustion Reaction
Like many organic compounds, methyl formate is highly flammable. When burned, it produces:
HCOOCH3+O2→CO2+H2OHCOOCH₃ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂OHCOOCH3+O2→CO2+H2O
Acidic and Basic Interactions
- In the presence of strong acids, methyl formate undergoes hydrolysis.
- With strong bases, it can form formate salts and methanol.
Synthesis and Production
Methyl formate is synthesized industrially and in laboratories through different methods.
Industrial Production
Industrially, methyl formate is produced by the reaction of methanol and carbon monoxide in the presence of a strong base as a catalyst:
CH3OH+CO→HCOOCH3CH₃OH + CO → HCOOCH₃CH3OH+CO→HCOOCH3
This reaction occurs under high pressure and temperature.
Laboratory Synthesis
In a lab, methyl formate can be made by esterification, where formic acid reacts with methanol in the presence of sulfuric acid:
HCOOH+CH3OH⇌HCOOCH3+H2OHCOOH + CH₃OH \rightleftharpoons HCOOCH₃ + H₂OHCOOH+CH3OH⇌HCOOCH3+H2O
Uses and Applications
Methyl formate has diverse applications across industries.
Industrial Applications
- Used as an intermediate in chemical synthesis
- Acts as a solvent in industrial processes
Role in Perfumes and Flavors
Due to its pleasant fruity odor, methyl formate is used in:
- Perfume manufacturing
- Flavoring agents for foods and beverages
Use in Pharmaceuticals
Methyl formate serves as a starting material in pharmaceutical synthesis.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Understanding the risks and handling of methyl formate is crucial for safe use.
Toxicity Levels
- Low toxicity at normal exposure levels
- Harmful if inhaled in large quantities
- Can cause irritation to the eyes and respiratory system
Environmental Risks
- Can contribute to air pollution when released in large amounts
- Breaks down quickly in the atmosphere
Safe Handling Practices for Methyl Formate (hcooch ch2 h2o)
Methyl formate is a useful chemical, but due to its flammability and toxicity at higher exposure levels, it requires careful handling to ensure safety in both industrial and laboratory environments. Below are detailed guidelines for handling methyl formate safely.
1. Proper Storage
To avoid any risks associated with methyl formate, storage must be done with specific precautions.
- Store in a cool, dry place: Methyl formate should be kept away from sources of heat or sunlight, as it is highly flammable.
- Use appropriate containers: Store methyl formate in containers made from materials that are compatible with esters, such as stainless steel or glass. Avoid storing it in containers made from aluminum or copper, which may react with the compound.
- Ventilated storage area: Make sure the storage area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of flammable vapors. Explosion-proof fans are a good idea in high-risk areas.
2. Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for anyone handling methyl formate.
- Gloves: Wear chemical-resistant gloves, preferably made from butyl rubber or neoprene, to protect the skin from contact.
- Eye Protection: Always wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from splashes or vapors. Methyl formate can irritate the eyes and cause severe damage if exposed for prolonged periods.
3. Handling and Transfer
The process of handling and transferring methyl formate should minimize the risk of exposure and accidents.
- Avoid open flames: As methyl formate is highly flammable, never work with it near open flames, sparks, or hot surfaces. Ensure there are no ignition sources in the vicinity.
- Use proper transfer equipment: When transferring methyl formate, use grounded equipment to avoid static charges, which can ignite vapors. Use sealed systems to minimize vapor release.
4. Ventilation
Ensure that the area where methyl formate is being used has adequate ventilation.
- Local exhaust ventilation (LEV): In laboratories or industrial settings, use fume hoods or local exhaust ventilation to remove vapors directly from the source. This prevents the buildup of harmful vapors in the workspace.
- Good general ventilation: In larger spaces, ensure there is proper airflow to prevent methyl formate vapors from accumulating, as they can be hazardous when inhaled.
5. Fire Safety
Due to the flammability of methyl formate, fire safety is critical.
- Fire extinguishers: Always have Class B fire extinguishers (for flammable liquids) readily available in the vicinity. Do not use water to extinguish a methyl formate fire, as it could worsen the situation. Instead, use foam or dry chemical extinguishers.
- Flame arrestors: For systems where methyl formate is transferred or stored, ensure that flame arrestors are installed to prevent any ignition from spreading through pipelines or containers.
Conclusion
Methyl formate hcooch ch2 h2o is an important ester with a wide range of uses in the chemical, fragrance, and pharmaceutical industries. Its flammability and toxicity require careful handling, but its industrial significance remains high.
Share this content:













Post Comment